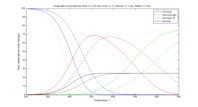
A comparison of combustion vs pyrolysis with a biochar feedback loop. The model was based on mass balance and reaction rates, and was patterned after a CFB reactor. Modeling was done in MATLAB. Conclusions were that pyrolysis does not match the net energy output that simple combustion can, but that other factors such as environmental or economic concerns may shift the balance in favor of pyrolysis.
Modeling Corn Stover Pyrolysis
ENGS 36 Chemical Engineering; December 2010
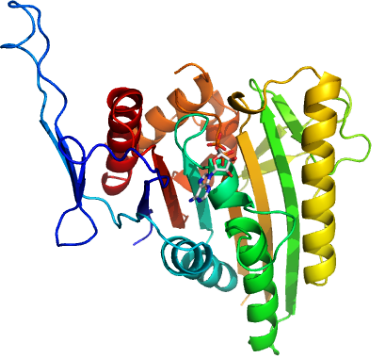
Costal2 Kinesin Mutagenesis
Presidential Scholar Research Assistant; June - December 2010
http://www.thesgc.org/structures/
Costal2 (Cos2) is a human kinesin in the critical Hedgehog Signaling Complex. Unlike most kinesins, Cos2 oligomerizes in solution, making characterization and determination of its structure difficult. This project involved the site-directed mutagenesis of Cos2 with the goal of obtaining monomeric Cos2 protein for x-ray crystallography and other characterization techniques.
Emissions from Two-Stroke Engines and the Effects of UV Light
CHEM 63 Environmental Chemistry; August 2010
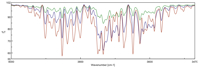
with Shimul Begum, Siobhan Hurley, Ruth McGovern
The effects of sunlight on exhaust components, specifically carbon dioxide (CO2), nitrogen oxides (NOX), carbon monoxide (CO), and hydrocarbons were analyzed under a controlled UV mercury lamp with a wavelength of 254 nm. Multiple samples of exhaust were collected from different two stroke engines and exposed to a UV mercury lamp. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy was then used in order to measure infrared spectra of absorption at different intervals of UV exposure. Analysis of the infrared spectra revealed shifting in the concentrations of several components of the exhaust. The concentrations of carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides and hydrocarbons all shifted considerably over hourly intervals. Overall, a decrease in carbon monoxide and hydrocarbons was observed, whereas the concentration of carbon dioxide and the nitrogen oxides increased. These shifts in concentration support the conclusion that exposure to UV light prompts the reaction of carbon monoxide with oxygen to produce carbon dioxide. Nitric oxide also reacts with oxygen in order to make nitrogen dioxides.
Project List
- * Nanoparticle Scavenging of ROS
- Biomineralization Review
- * Micro-syringe Design
- COF-CNT Nanocomposite Proposal
- MAPLE Review
- 3D Micromachining Review
- * Photovoltaics for Space
- * Conducting Polyaniline Nanofibers
- * Translumenal Endoscopic Device
- Modeling Corn Stover Pyrolysis
- * Cos2 Kinesin Mutagenesis
- * Emissions from Two-Stroke Engines
- Note: * indicates hands-on lab or design experience














